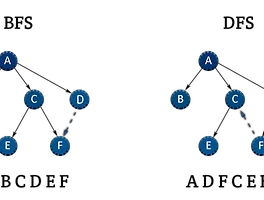
플러드 필
어떤 위치와 연결된 모든 위치를 찾는 알고리즘
연결 요소를 찾기와 유사한 문제 -> 그래프 문제
그렇지만 인접 행렬이나 리스트 만들 필요 없다, 단순히 주어진 이차원 배열을 통해 dfs, bfs로 탐색하면 모든 문제를 해결할 수 있다.
1. 단지번호 붙이기
문제 : https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2667
2667번: 단지번호붙이기
<그림 1>과 같이 정사각형 모양의 지도가 있다. 1은 집이 있는 곳을, 0은 집이 없는 곳을 나타낸다. 철수는 이 지도를 가지고 연결된 집들의 모임인 단지를 정의하고, 단지에 번호를 붙이려 한다. 여기서 연결되었다는 것은 어떤 집이 좌우, 혹은 아래위로 다른 집이 있는 경우를 말한다. 대각선상에 집이 있는 경우는 연결된 것이 아니다. <그림 2>는 <그림 1>을 단지별로 번호를 붙인 것이다. 지도를 입력하여 단지수를 출력하고, 각 단지에 속하는 집의 수
www.acmicpc.net
풀이
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
vector<vector<int>> graph;
vector<vector<bool>> check;
vector<int> ans;
int n;
void dfs(int,int, int);
int main() {
cin >> n;
// graph 채우기
graph.assign(n, vector<int>(n, 0));
check.assign(n, vector<bool>(n, false));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
scanf("%1d", &graph[i][j]);
}
// 탐색
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
if (graph[i][j] == 1 && check[i][j]==false)
dfs(i, j, 0);
// 출력
cout << ans.size() << "\n";
sort(ans.begin(), ans.end());
for (int i = 0; i < ans.size(); i++)
cout << ans[i]<<"\n";
return 0;
}
void dfs(int x, int y, int cnt) {
if (cnt == 0 && check[x][y] == false) {
ans.push_back(0);
}
check[x][y] = true;
ans[ans.size() - 1] += 1;
// 4방향 체크
// 왼쪽 이동
if (x - 1 >= 0 && check[x - 1][y] == false && graph[x-1][y]==1)
dfs(x - 1, y, cnt + 1);
// 오른쪽 이동
if (x + 1 <= n-1 && check[x + 1][y] == false && graph[x + 1][y] == 1)
dfs(x + 1, y, cnt + 1);
// 위로 이동
if (y - 1 >= 0 && check[x][y - 1] == false && graph[x][y-1] == 1)
dfs(x, y - 1, cnt + 1);
// 아래로 이동
if (y + 1 <= n - 1 && check[x][y + 1] == false && graph[x][y+1] == 1)
dfs(x, y + 1, cnt + 1);
}
BFS를 통해 문제 해결하기(가장 중요한 부분)
BFS의 기본적인 목표는 임의의 정점에서 시작해서 모든 정점을 한 번씩 방문하는 것이다.
그러나 특정한 조건이 만족할 때 BFS는 최단 거리를 구하는 알고리즘이 될 수 있다.
그 이유는 단계 별로 진행되기에 특정 조건이 만족되면 최단 거리를 구할 수 있다.
<조건>
1) 최소 비용 문제
2) 간선 가중치 1
3) 정점과 간선의 개수가 적어야 한다(시간, 메모리 제한)
2. 미로 탐색
문제 : https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2178
2178번: 미로 탐색
첫째 줄에 두 정수 N, M(2 ≤ N, M ≤ 100)이 주어진다. 다음 N개의 줄에는 M개의 정수로 미로가 주어진다. 각각의 수들은 붙어서 입력으로 주어진다.
www.acmicpc.net
풀이
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
vector<vector<int>> graph;
vector<vector<bool>> check;
vector< vector<int>> ans;
int n, m;
void bfs(int, int);
int main() {
cin >> n >> m;
// graph 채우기
graph.assign(n, vector<int>(m, 0));
check.assign(n, vector<bool>(m, false));
ans.assign(n, vector<int>(m, 0));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
scanf("%1d", &graph[i][j]);
}
bfs(0, 0);
cout << ans[n - 1][m - 1] + 1;
return 0;
}
// bfs
void bfs(int x, int y) {
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push(pair<int,int>(x,y));
check[x][y] = true;
// Q가 빌때 까지
while (!q.empty()) {
pair<int, int> now;
now = q.front();
q.pop();
int now_x = now.first;
int now_y = now.second;
// 왼쪽 이동
if (now_x - 1 >= 0 && graph[now_x - 1][now_y] == 1 && check[now_x - 1][now_y] == false) {
check[now_x - 1][now_y] = true;
pair<int, int> temp(now_x - 1, now_y);
ans[now_x - 1][now_y] = ans[now_x][now_y] + 1; // 값 +1
q.push(temp);
}
// 오른쪽 이동
if (now_x + 1 < n && graph[now_x + 1][now_y] == 1 && check[now_x + 1][now_y] == false) {
check[now_x + 1][now_y] = true;
pair<int, int> temp(now_x + 1, now_y);
ans[now_x + 1][now_y] = ans[now_x][now_y] + 1; // 값 +1
q.push(temp);
}
// 위쪽 이동
if (now_y - 1 >= 0 && graph[now_x][now_y-1] == 1 && check[now_x][now_y-1] == false) {
check[now_x][now_y-1] = true;
pair<int, int> temp(now_x, now_y-1);
ans[now_x][now_y-1] = ans[now_x][now_y] + 1; // 값 +1
q.push(temp);
}
// 아래쪽 이동
if (now_y+1 < m && graph[now_x][now_y+1] == 1 && check[now_x][now_y+1] == false) {
check[now_x][now_y+1] = true;
pair<int, int> temp(now_x, now_y+1);
ans[now_x][now_y+1] = ans[now_x][now_y] + 1; // 값 +1
q.push(temp);
}
}
}'Archived(CSE Programming) > 알고리즘(C++)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 다이나믹 프로그래밍 문제 (0) | 2019.08.25 |
|---|---|
| 다이나믹 프로그래밍(Dynamic Programming) (0) | 2019.08.22 |
| 그래프의 탐색(DFS, BFS) (0) | 2019.08.15 |
| 그래프(Graph) (0) | 2019.08.14 |
| 브루트포스-N과 M (0) | 2019.08.14 |